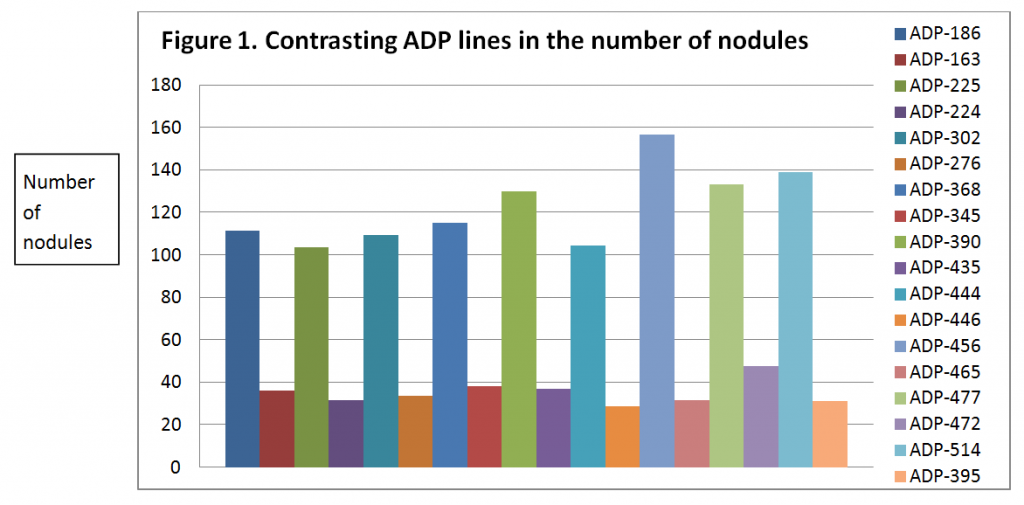
This study examined the nodulation characteristics of 400 lines from the Andean Diversity Panel (ADP). Inoculation with Rhizobium tropici strain CIAT 899 and Rhizobium etli CIAT 632 was carried out in a screenhouse using pasteurized sand in benches. Ten seeds per cultivar/line were sown from each line after surface disinfection with 10% bleach, followed by rinses with sterile water. The Rhizobium strains were grown individually in a Yeast Mannitol Broth Media. Five days after sowing the seedlings, they were inoculated with 1 ml of 1 x 109 rhizobia cells/ml. Rhizobia counts were conducted with a hematocytometer and the estimation of the viable rhizobia cells was carried out in Yeast Mannitol Agar using the drop plate method. The inoculation consisted of applying 1 ml of the Rhizobium broth culture of each strain separately onto the stem of each seedling. Cultivar Verano was included as a local check with each group of ten lines evaluated in sequential plantings. Nodulation was evaluated 12 days after inoculation by counting the nodules in the upper 3 cm of the roots and the location of the upper-most nodule (UMN) was measured in cm. In the combined analysis for both Rhizobium strains, the results showed contrasting results in nodule numbers resulting from the inoculation with R. tropici and R. etli with 134 different ADP lines (Figure 1). Lines that formed the greatest number of nodules 12 days after inoculation in the upper 3 cm of the root are shown in contrast with ADP lines that had the lowest number of nodules (Figure 1).
Even though all 134 ADP lines nodulated with both strains, significant differences (P > 0.05) were found between Rhizobium tropici and Rhizobium etli in the number of nodules produced by each strain (Figure 2). The 134 ADP lines produced the highest number of nodules with Rhizobium etli. These findings are particularly important since reports indicate that Andean genotypes prefer R. etli over R. tropici. However, from the 134 ADP lines, ADP-390, 456 and 514 nodulated better with R. tropici than with R. etli. The outstanding lines for overall nodulation were ADP-186, 225, 302, 368, 390, 444, 456, 477 and 514.